In vitro fertilization is a form of treatment applied to women who cannot conceive with classical methods

Yavuz Aydın MD Prof.
GYNECOLOGY, OBSTETRICS AND IVF SPECIALIST
GYNECOLOGY, OBSTETRICS AND IVF SPECIALIST
Treatments
01

02

03
Pregnancy Calculator
About me
Yavuz Aydın MD Prof.
Yavuz Aydın MD Prof. gradueted from Hacettepe University medical faculty in 1993. He completed hıs obstetrics and gynecology residency ın Istanbul university, Cerrahpasa Medıcal Faculty between 1994-1999. Than, he worked as obstetrician and gynecologıst ın Medicana health group and returned to Istanbul unıversıty to focuse on gynecologic endocrınology and infertility in 2007. He completed ivf treatment in Cerrahpasa Medical Faculty and had the degree of associate professor in 2012.

İ.A.Ü. VM Medical Park Florya Hospital
0542 640 21 12
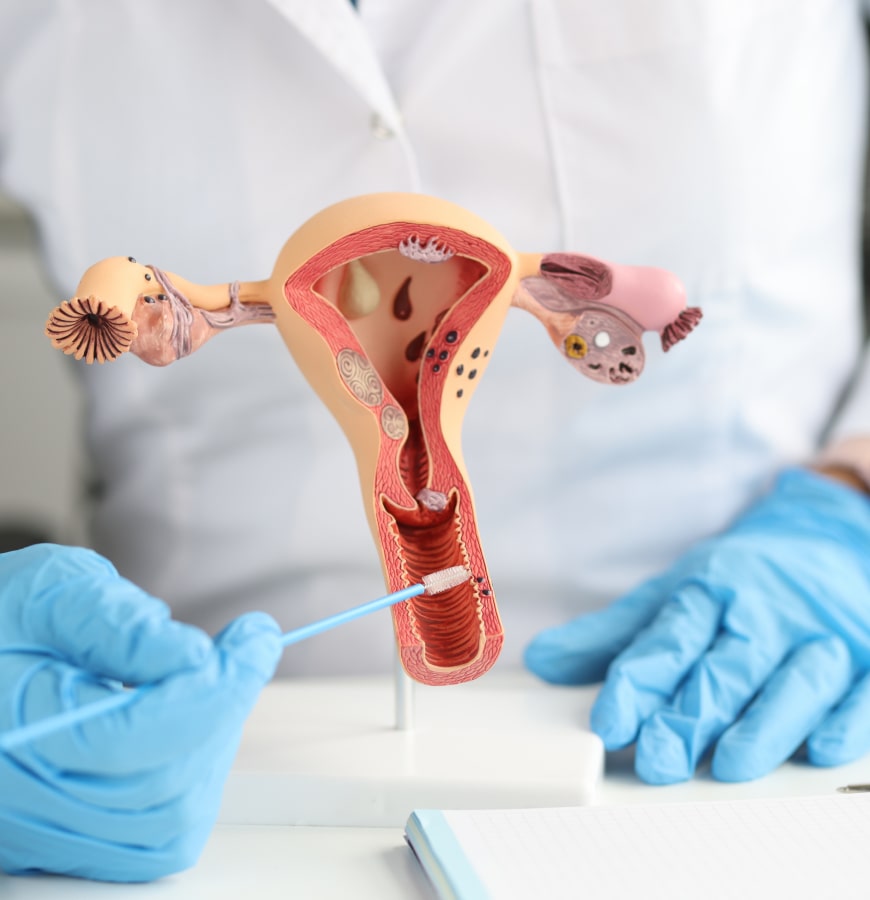
IVF Treatment
What is IVF Treatment?
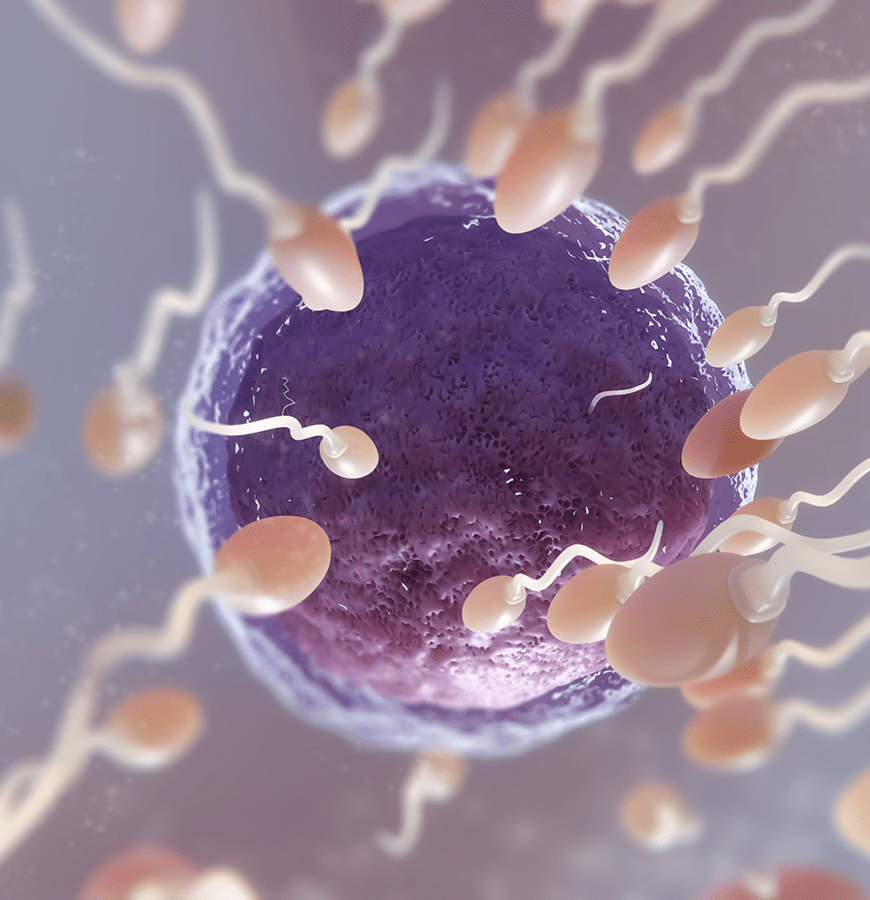
To briefly summarize the IVF application, we can explain it as the fertilization process of male and female reproductive cells under in vitro conditions. In this method, male and female reproductive cells are kept in a suitable environment at body temperature for 48 hours. Fertilization occurs in about half of the eggs obtained during this period. These fertilized eggs are called embryos (fetus) and are placed into the female uterus, which is the final destination.
Detailed Info

STEP BY STEP
In vitro fertilization Treatment
1

Ovarian Alert
2
Ovarian Removal
3
Fertilization
Plan your treatment and get a price quote online
30 minutes of free online video or telephone consultation
Why Turkey?
Why is Turkey
So popular
In medical tourism?
So popular
In medical tourism?
Health tourism refers to people traveling between countries for healthcare services. These services include surgeries, treatment, examinations and other healthcare services.
Airport transfer is a service used to provide transportation for people engaged in health tourism. This service enables the person to reach the place where he/she will receive healthcare service or the place where he/she will stay from the airport. The airport transfer service is provided by a pre-arranged vehicle or taxi, rather than using one's own car. This service is usually offered by the health facility or provided by private transfer service companies. Thanks to this service, the person will be able to reach the country they are traveling to for healthcare service in a comfortable and peaceful way during the arrival or departure.
Airport transfer is a service used to provide transportation for people engaged in health tourism. This service enables the person to reach the place where he/she will receive healthcare service or the place where he/she will stay from the airport. The airport transfer service is provided by a pre-arranged vehicle or taxi, rather than using one's own car. This service is usually offered by the health facility or provided by private transfer service companies. Thanks to this service, the person will be able to reach the country they are traveling to for healthcare service in a comfortable and peaceful way during the arrival or departure.
Videos
Your doctor Explains
 en
en